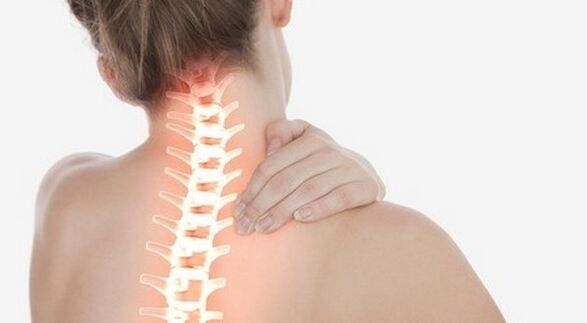
Headaches, dizziness, flickering in the eyes - these are the first signs that signal possible problems with the cervical spine.The symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis are so ambiguous that the pathology is often confused with other diseases.Therefore, it is important to know the main signs of the disease and methods of dealing with its complications.
The essence of the pathological phenomenon
Osteochondrosis in the cervical spine is expressed by degenerative-dystrophic phenomena affecting the cervical intervertebral discs.Destructive processes are observed, as a rule, in the moving part of the neck.
The vertebrae in this part of the spine are closely spaced together.The neck frame is not particularly mobile, and this increases the risk of vertebral displacement and pinched nerve endings.
Compression of the vertebral artery causes cerebrovascular accident.These factors destabilize blood flow in the vertebral artery lead to spinal ischemia.
Poor circulation reduces the sensitivity of the neck muscles and causes weakness.Pathology acts as a factor provoking protrusions and hernias, which also impinge on nerve endings, causing them to swell.The nerve root covers the entire cervical-vertebral canal, and this puts additional pressure directly in the canal itself.This course of pathology is expressed through acute pain and exacerbation of the disease.
General characteristics of the signs of the disease
Medical research shows that symptoms associated with problems in the cervical spine may not appear at the beginning of their development.As the disease develops, the patient may experience acute pain when moving the head and neck.
Vestibular disorders
Another manifestation of pathology in men and women may be nausea, which is provoked by cerebrovascular accident.Vomiting often begins, which can be caused by deterioration of blood flow through the arteries and lack of oxygen in the inner ear, where the balance point is located.
Another symptom of the disease in men and women may be a lack of air, which occurs when the phrenic nerve, which is part of the cervical plexus, is irritated.A person may experience hypoxia, which causes them to feel weak in their muscles in the morning.
Symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis include such phenomena as noise or ringing in the ears, flickering in the eyes.The vestibular apparatus is filled with blood exclusively from the vertebral artery, so tinnitus is a common occurrence.In addition to these sensations, the patient begins to suffer from a decrease in the overall level of hearing.Collectively, these symptoms are defined as cochlear syndrome.
Considering that the visual analyzer is fed not only by the vertebral artery, but also by the carotid artery, visual impairment is rare.Atherosclerosis of the arteries of the brain or low blood pressure leads to signs of decreased vision.With the development of cervical osteochondrosis, the following symptoms are possible:
- flickering in the eyes;
- change of focus;
- decreased visual acuity and blurred vision.
If the flow of cerebral circulation is disrupted, patients may lose consciousness.
This condition is caused by spasm of the vertebral artery, which occurs as a reaction to irritation of the nerve roots and deformed protrusions of the vertebrae.
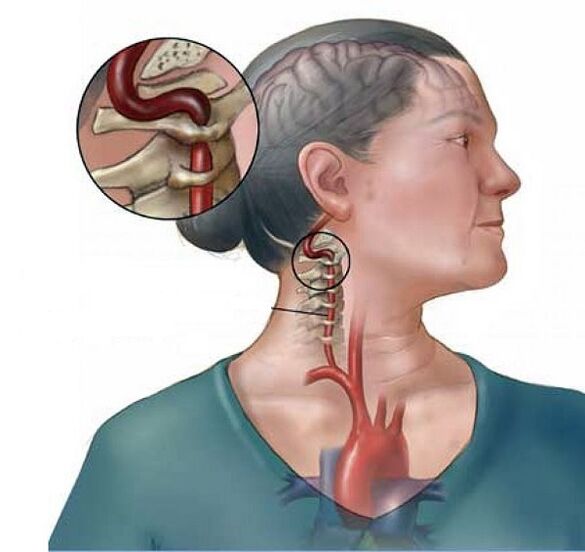
To restore the patient’s normal well-being, it is necessary to give the body a horizontal position and raise the legs.This measure increases the flow of venous blood to the lower extremities and improves the state of cerebral circulation in the vertebral artery.
Changes in blood pressure cause circulatory problems in the medulla oblongata, where the vascular plexus area is located.
Dizziness is a common symptom of the disease, which manifests itself due to a lack of oxygen supply to the semicircular tubules of the inner ear, which are responsible for the state of balance.
Classification of symptoms and stages of pathology
All the main symptoms of pathology of the cervical spine can be divided into groups of syndromes:
- Radicular.
- Ischemic.
- Vertebral artery.
- Vegetative-vascular.
- Reflex.

The nature of the course and severity of the disease allow doctors to distinguish three stages of development of the pathology.
At the first stage, the capsule of the cervical intervertebral disc of the spine ruptures.In this case, the characteristic manifestations of the pathology are headaches, pain in the neck and shoulders, limited mobility in this area, and decreased sensitivity of the skin of the collar area.Another alarming symptom is flickering in the eyes.Pain at this stage of the disease is in the nature of electrical discharges.
Also at this stage, Wright's syndrome may develop, manifested by numbness and tingling in the pathological area.
The second syndrome that develops with the disease is cervicalgia syndrome.This exacerbation occurs in cases where inflammation affects muscle tissue.
Anterior scalene syndrome includes a group of symptoms that occur when the inferior roots of the brachial plexus and subclavian artery are pinched.
At the second stage, a disruption of the connections between the discs occurs, which is accompanied by a decrease in the distance between the vertebrae and drying out of the fibrous ring.
At this stage, severe pain with a crunch appears, muscle weakness, flickering in the eyes increases, and the clarity of tendon reflexes decreases.In addition, there is pain radiating to the scapula area.The patient suffers from headaches and insomnia.

The second stage of the disease lasts several years.Periodic exacerbation of the pathology causes falling head syndrome and blurred vision.
At the third stage, a change in the structure of tissues and intervertebral discs occurs.At this stage, the vertebral body is completely ruptured, the corpus pulposus falls out and a hernia is formed.
Symptoms of this stage are characterized by the following:
- sharp pain;
- paralysis of the shoulder muscles;
- curvature of the spinal column;
- lack of sensitivity in the neck and shoulder area.
At this stage of development of the disease, complications such as paralysis or paresis develop due to impaired cerebral circulation.
Complications
The consequences of the development of neck pathology can be divided into several groups.
The first group includes complications of a mechanical nature.These include displacement of intervertebral discs, the formation of osteophytes, a decrease in vertebral height, and the formation of a hernia.
As a rule, such complications cause an advanced state of the disease and an exacerbation that is not treated in time.
The second group of consequences are complications that affect the condition of blood vessels.Impaired cerebral circulation due to infringement of the vertebral artery leads to the development of paralysis of the entire spine, the appearance of dizziness, and flickering in the eyes.
The third group is complications of a neurological nature, among which the main ones can be identified:
- diencephalic syndrome, which develops against the background of dysfunction of the hypothalamus.In this case, the patient is susceptible to neurotic conditions, his headaches become more frequent, and his body feels weak;
- drop syndrome.In such a situation, the patient may experience sudden fainting.Loss of consciousness is preceded by headaches and tinnitus;
- laryngeal syndrome.With these complications, the sonority of the voice decreases;
- blurred vision.This complication appears as a result of constriction of cerebral circulation in the cervical spine due to compression of the vertebral artery.The patient experiences flickering in the eyes and pain in the neck.

We begin to fight the disease
Exacerbation of cervical osteochondrosis is accompanied by severe pain, so first aid consists of pain relief.You can take analgesics and apply ointments containing anti-inflammatory components to the affected area.
The doctor may also inject relaxing medications into the pain area.Such assistance is necessary to relax muscles and relieve tension.Weakness appears in the body, but spasm and soreness go away.
Exacerbation of the disease can be eliminated with blockades, which reduce acute pain and reduce its intensity.
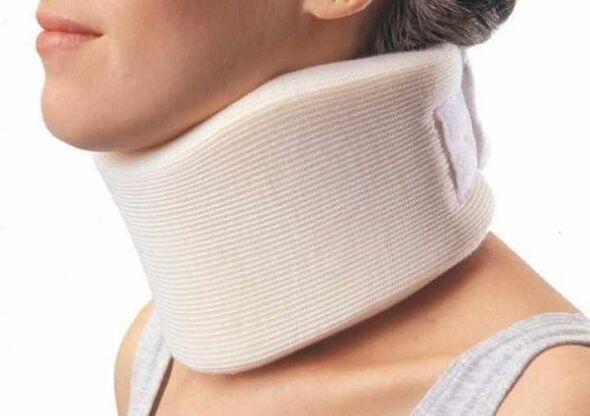
In an inpatient setting, the doctor determines which treatment methods should be used for a particular situation.Drug therapy to eliminate the symptoms of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine involves taking anti-inflammatory non-steroidal drugs and muscle relaxants.To reduce the load on the neck area, doctors recommend wearing a Shants collar.
Neck traction may be performed in the hospital.As a result of this procedure, the distance between the vertebrae increases and the degree of compression of the vertebral artery decreases.
Gymnastics as a method of treatment
Considering that dystrophic changes occur against the background of destruction, it is necessary to pay attention to physical exercise.To eliminate the symptoms of the disease, you can play sports.Exercise therapy, yoga, and Pilates have a positive effect on the problem of the spine.You can play sports only after pain has been eliminated.If an exacerbation occurs, it is better to refrain from playing sports.
Playing sports should be under the supervision of specialists, since the cervical spine area is sensitive, and any damage is life-threatening.Physical activity eliminates muscle weakness, reduces the level of stiffness in spinal movements, and eliminates circulatory disorders.You can also do physical therapy at home, having first received the recommendations of a specialist.
The disease should be combated at the stage of its inception in order to prevent an exacerbation of its manifestations.The symptoms that appear signal the need for treatment, since any changes lead to serious consequences.